
- #Computer network architect upgrade#
- #Computer network architect software#
Communicate with vendors to gather information about products, alert them to future needs, resolve problems, or address system maintenance issues.Develop and write procedures for installation, use, or troubleshooting of communications hardware or software.Maintain or coordinate the maintenance of network peripherals, such as printers.
#Computer network architect software#
Use network computer-aided design (CAD) software packages to optimize network designs. Develop or maintain project reporting systems. Explain design specifications to integration or test engineers. Coordinate installation of new equipment. Develop plans or budgets for network equipment replacement. Prepare or monitor project schedules, budgets, or cost control systems. Design, build, or operate equipment configuration prototypes, including network hardware, software, servers, or server operation systems. 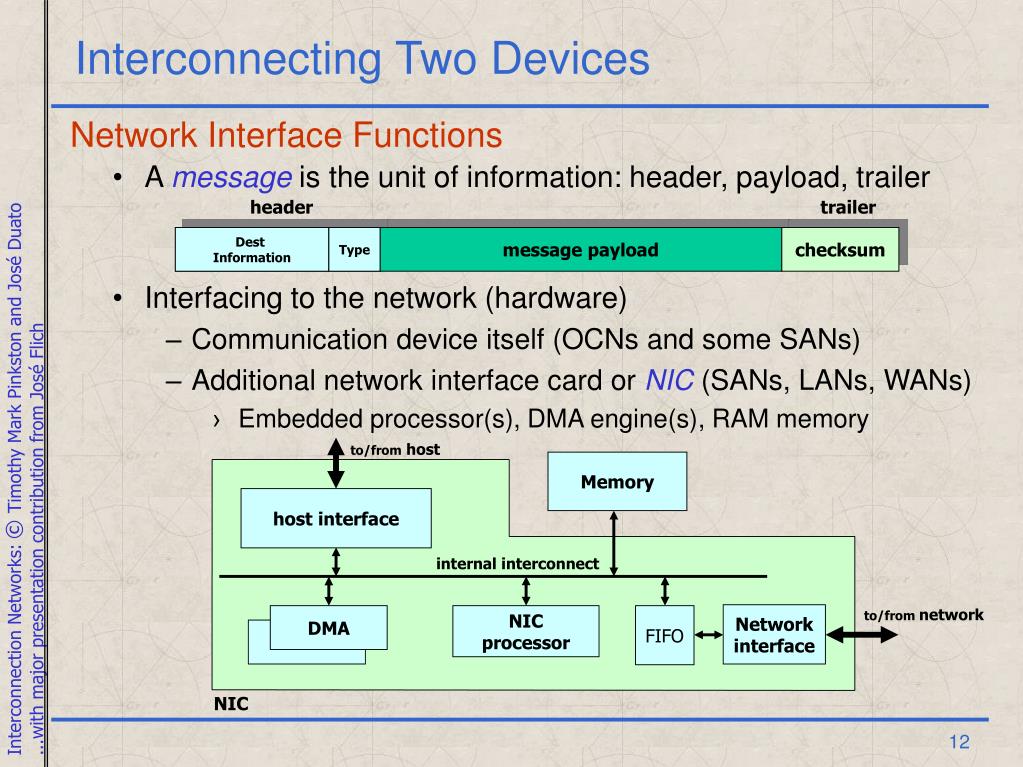 Prepare design presentations and proposals for staff or customers. Communicate with customers, sales staff, or marketing staff to determine customer needs. Research and test new or modified hardware or software products to determine performance and interoperability. Develop procedures to track, project, or report network availability, reliability, capacity, or utilization. Coordinate network operations, maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. Supervise engineers or other staff in the design or implementation of network solutions. Estimate time and materials needed to complete projects. Prepare detailed network specifications, including diagrams, charts, equipment configurations, or recommended technologies. Adjust network sizes to meet volume or capacity demands.
Prepare design presentations and proposals for staff or customers. Communicate with customers, sales staff, or marketing staff to determine customer needs. Research and test new or modified hardware or software products to determine performance and interoperability. Develop procedures to track, project, or report network availability, reliability, capacity, or utilization. Coordinate network operations, maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. Supervise engineers or other staff in the design or implementation of network solutions. Estimate time and materials needed to complete projects. Prepare detailed network specifications, including diagrams, charts, equipment configurations, or recommended technologies. Adjust network sizes to meet volume or capacity demands. #Computer network architect upgrade#
Participate in network technology upgrade or expansion projects, including installation of hardware and software and integration testing. Evaluate network designs to determine whether customer requirements are met efficiently and effectively. Visit vendors, attend conferences or training sessions, or study technical journals to keep up with changes in technology. Communicate with system users to ensure accounts are set up properly or to diagnose and solve operational problems. Determine specific network hardware or software requirements, such as platforms, interfaces, bandwidths, or routine schemas. Develop and implement solutions for network problems. Develop conceptual, logical, or physical network designs. Coordinate network or design activities with designers of associated networks. Monitor and analyze network performance and reports on data input or output to detect problems, identify inefficient use of computer resources, or perform capacity planning. Develop or recommend network security measures, such as firewalls, network security audits, or automated security probes. New approaches are necessary, ones that require transformational changes in how networks are architected. Traditional, manually intensive methods of managing computer networks are proving to be unsustainable. Networks also need to be dynamic, agile, and in lockstep with business needs. WANs need to minimize costs and enhance user experience when serving distributed applications to distributed users. Data center networks need to connect applications in multiple data centers and clouds. Today, to serve the exacting needs brought on by technology advancements and digital transformation initiatives, networks are called on to do more.Īccess networks need to recognize, authenticate, and authorize user devices and smart things before bringing them on board. Why are network architectures under pressure? To accommodate these varied requirements, all network types have unique architectures. 
These and all other networks face different security threats, which they need to guard against. Wide-area networks (WANs) connect users to applications, sometimes over long distances, such as connecting hospital workers to health applications.Networks for data center connect servers that host data and applications and make them available to users.Access networks, for campuses and branches, are built to bring users and things onboard, such as connecting employees within an office building.Described below are three common types of enterprise networks: Why are there different network architectures?Ĭomputer networks are built to serve the needs of their clients.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
